Understanding Metronidazole: A Guide for Veterinary Professionals
Published on:
2024-02-24
Metronidazole is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication that is widely used in veterinary medicine to treat bacterial and parasitic infections in animals. It is effective against a wide range of organisms, including anaerobic bacteria, protozoa, and some parasites. In veterinary practice, metronidazole is commonly prescribed to treat conditions such as gastrointestinal infections, periodontal
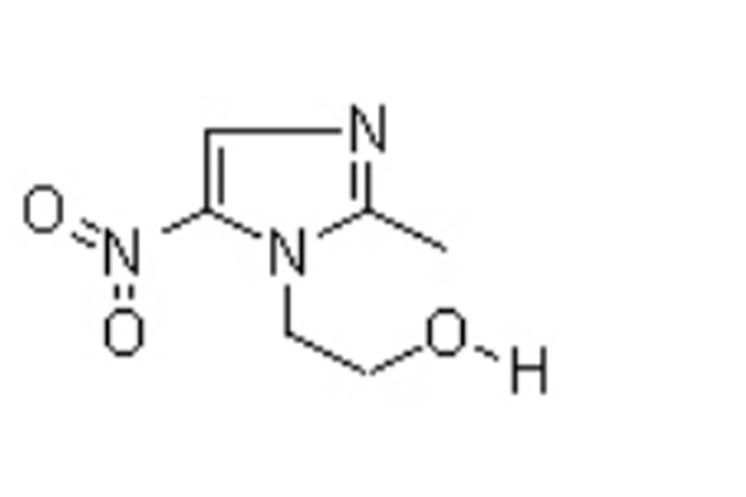
Metronidazole is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication that is widely used in veterinary medicine to treat bacterial and parasitic infections in animals. It is effective against a wide range of organisms, including anaerobic bacteria, protozoa, and some parasites.
In veterinary practice, metronidazole is commonly prescribed to treat conditions such as gastrointestinal infections, periodontal disease, and certain types of skin infections. It is also used in the treatment of certain types of diarrheal diseases and to prevent infections after certain surgical procedures.
When prescribing metronidazole to animal patients, veterinary professionals should be aware of the potential side effects and drug interactions associated with the medication. Common side effects of metronidazole in animals include nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. In some cases, metronidazole can also cause neurotoxicity, particularly in high doses or with prolonged use.
It is important for veterinary professionals to carefully consider the dosage and duration of treatment when prescribing metronidazole to animal patients, as inappropriate use of the medication can lead to resistance and treatment failure. Veterinary professionals should also be aware of any contraindications to the use of metronidazole in certain animal species or in animals with specific health conditions.
Overall, metronidazole is a valuable medication in the veterinary arsenal for the treatment of bacterial and parasitic infections in animals. By understanding its uses, potential side effects, and considerations for use, veterinary professionals can effectively incorporate metronidazole into their treatment protocols to provide optimal care for their animal patients.
In veterinary practice, metronidazole is commonly prescribed to treat conditions such as gastrointestinal infections, periodontal disease, and certain types of skin infections. It is also used in the treatment of certain types of diarrheal diseases and to prevent infections after certain surgical procedures.
When prescribing metronidazole to animal patients, veterinary professionals should be aware of the potential side effects and drug interactions associated with the medication. Common side effects of metronidazole in animals include nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. In some cases, metronidazole can also cause neurotoxicity, particularly in high doses or with prolonged use.
It is important for veterinary professionals to carefully consider the dosage and duration of treatment when prescribing metronidazole to animal patients, as inappropriate use of the medication can lead to resistance and treatment failure. Veterinary professionals should also be aware of any contraindications to the use of metronidazole in certain animal species or in animals with specific health conditions.
Overall, metronidazole is a valuable medication in the veterinary arsenal for the treatment of bacterial and parasitic infections in animals. By understanding its uses, potential side effects, and considerations for use, veterinary professionals can effectively incorporate metronidazole into their treatment protocols to provide optimal care for their animal patients.
Key words:

